The speedy developments in quantum computing which sparked rising considerations inside the cryptocurrency sector late final 12 months, notably concerning Bitcoin’s long-term resilience appear to have as soon as once more resurfaced.
CryptoQuant, an on-chain information analytics platform, just lately highlighted these dangers in a sequence of posts on X titled “Quantum Computing is a Rising Threat for Bitcoin”.
The dialogue centered on two vital features: Bitcoin mining safety and personal key vulnerabilities, each of which might face vital challenges as quantum applied sciences progress.
Quantum Threats to Bitcoin Mining and Community Safety
Bitcoin’s proof-of-work (PoW) system depends on computational energy to validate transactions and safe the community. The SHA-256 hash perform, integral to Bitcoin mining, at the moment ensures sturdy safety by, stopping malicious actors from tampering with the blockchain.
Nevertheless, CryptoQuant warns that quantum algorithms, particularly leveraging superior algorithms corresponding to Grover’s, might considerably “speed up hash-solving processes.”
If quantum computer systems grow to be able to outperforming classical mining {hardware}, it might tilt the steadiness of energy in mining, enabling quantum-equipped miners to dominate block validation. This dominance wouldn’t solely disrupt community consensus but in addition doubtlessly compromise Bitcoin’s decentralized construction.
CryptoQuant emphasizes the significance of sustaining a big share of non-quantum computing hash energy within the community. A wholesome and various mining ecosystem would mitigate the dangers posed by any entity gaining disproportionate management by way of quantum know-how.
Whereas quantum supremacy in mining stays speculative at this stage, the continuing developments within the discipline warrant shut monitoring by stakeholders, together with miners and builders.
Non-public Key Safety: Vulnerabilities And Variations
Past mining, quantum computing additionally presents dangers to BTC’s non-public key safety. The Bitcoin community makes use of cryptographic programs to safe wallets and transactions, with private and non-private keys forming the idea of possession.
In accordance with CryptoQuant, Shor’s Algorithm might theoretically enable quantum computer systems to infer non-public keys from public keys, thereby compromising pockets safety.
Notably susceptible are Pay-to-Public-Key (P2PK) addresses, the place the general public key straight serves because the pockets handle. In distinction, Pay-to-Public-Key-Hash (P2PKH) addresses present a further layer of safety by hashing public keys.
Non-public Key Safety & Quantum Dangers
One other main concern is Shor’s Algorithm, which might, in principle, enable quantum computer systems to search out non-public keys from public keys. ‘Pay to public key’ (P2PK) addresses are most susceptible to quantum assaults, as the general public key serves straight… pic.twitter.com/q2NBvbwGLe
— CryptoQuant.com (@cryptoquant_com) January 7, 2025
Nevertheless, when BTC from these addresses is transferred, the general public secret’s uncovered, growing susceptibility to quantum assaults. CryptoQuant additionally noticed a notable improve in P2PKH handle utilization, rising by 14% in latest months.
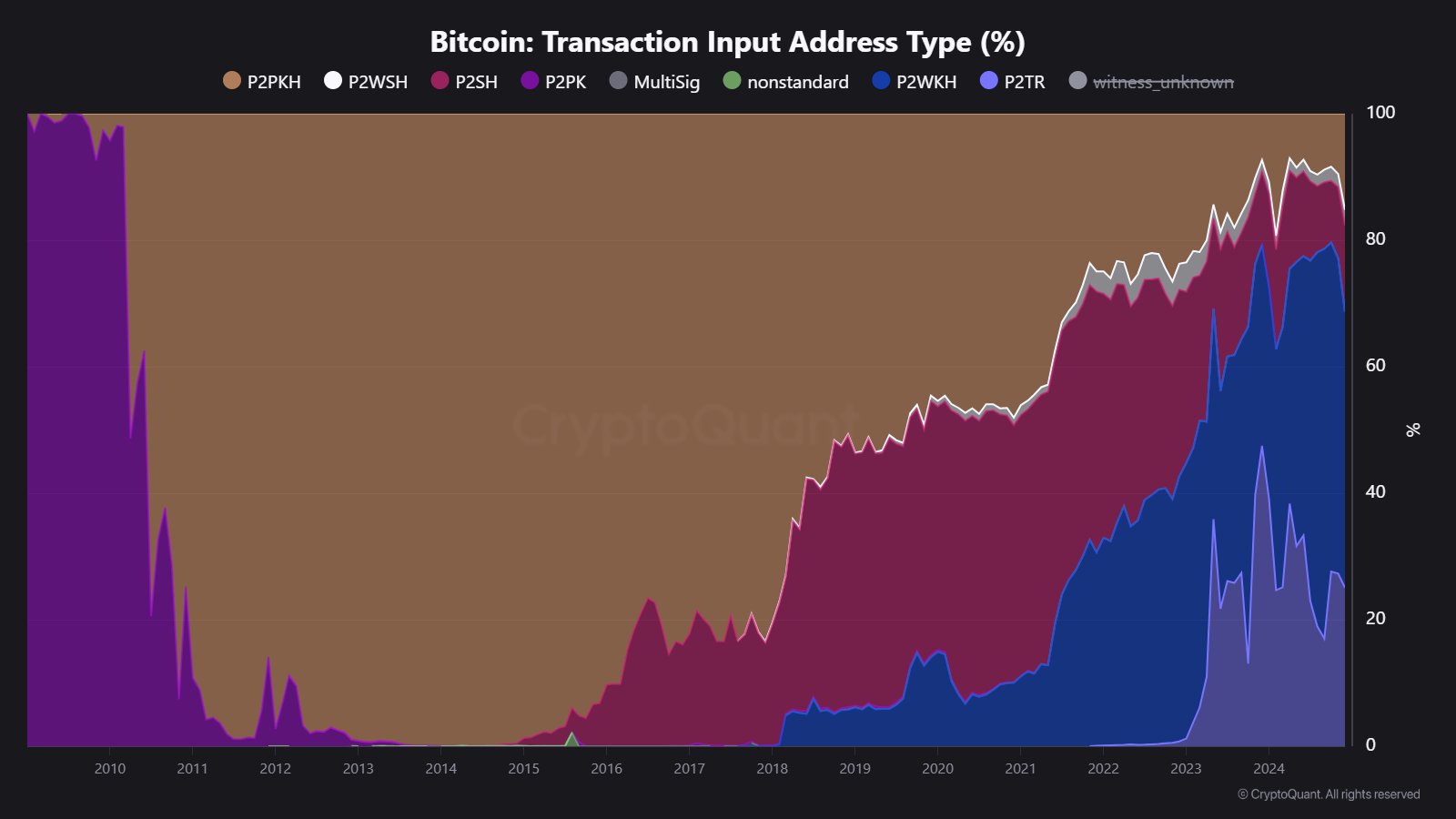
Whereas the precise explanation for this shift stays unclear, it suggests heightened consciousness and warning amongst Bitcoin holders concerning quantum vulnerabilities.
Featured picture created with DALL-E, Chart from TradingView











